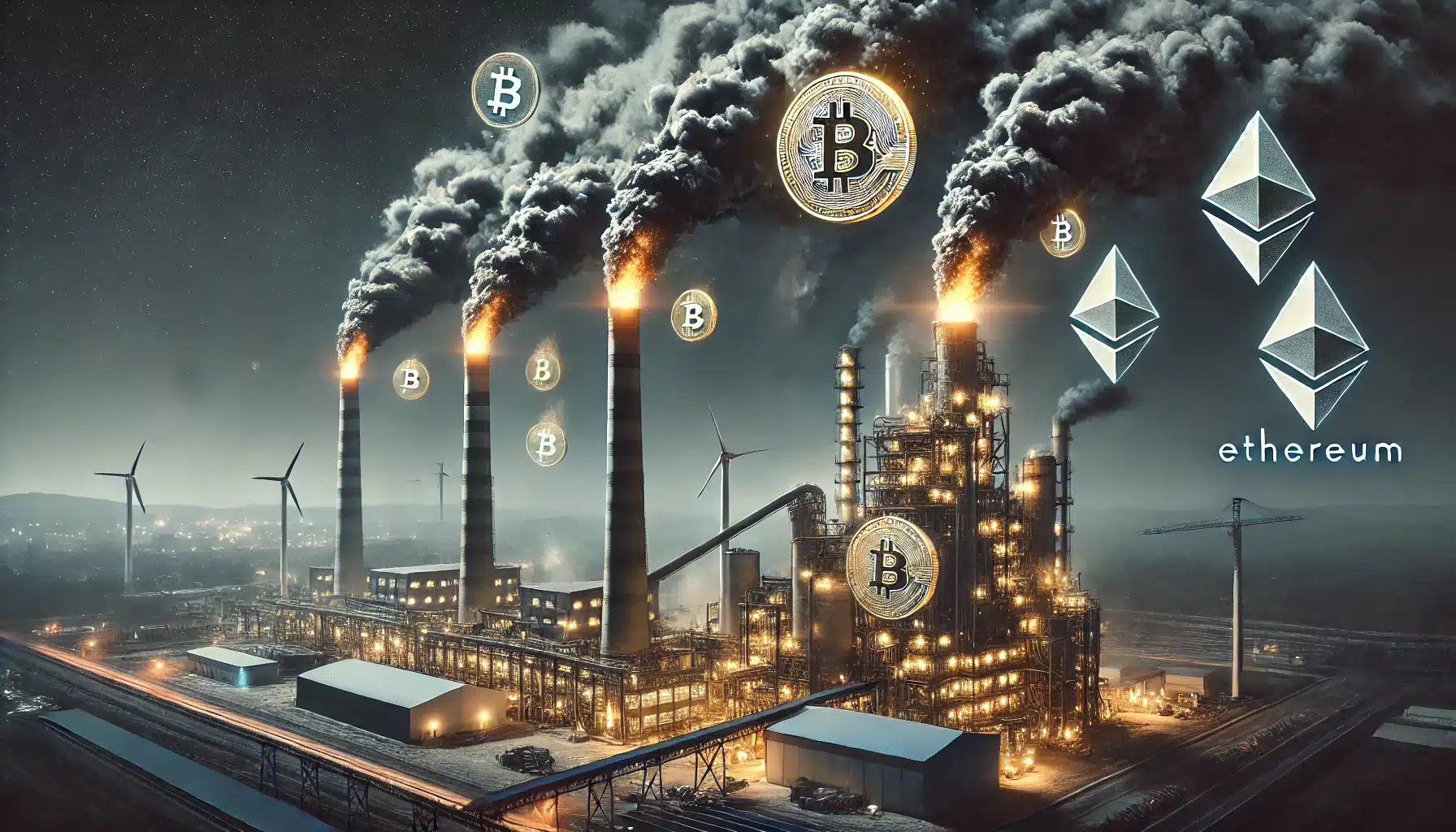
1. The Growing Concern Over Cryptocurrency’s Environmental Impact
As cryptocurrency continues to grow in popularity, so do concerns about its environmental impact. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other digital currencies rely on blockchain technology, which requires significant computational power to maintain network security and validate transactions. This process, particularly in Proof of Work (PoW) systems, is energy-intensive and has led to criticisms regarding the sustainability of cryptocurrencies. As the world increasingly focuses on combating climate change, the environmental impact of digital currencies has become a hot topic, prompting discussions about how to make blockchain technology more sustainable.
Why It Matters
Understanding the environmental impact of cryptocurrency is crucial for the future of digital assets. As more individuals and institutions adopt cryptocurrencies, finding ways to reduce their carbon footprint will be key to ensuring their long-term viability in a world that prioritizes sustainability.
2. The Environmental Footprint of Cryptocurrency: Energy Consumption and Carbon Emissions
The environmental impact of cryptocurrency is most often associated with its energy consumption. The process of mining, particularly for Bitcoin, is extremely energy-intensive due to the computational power required to solve complex mathematical problems.
2.1 Bitcoin Mining and Energy Use
Bitcoin mining relies on Proof of Work, where miners compete to solve cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions and secure the network. This process requires powerful hardware and vast amounts of electricity. According to the Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index, Bitcoin’s annual energy consumption is comparable to that of some entire countries.
- Why It Matters: The high energy consumption of Bitcoin mining contributes to significant carbon emissions, particularly if the electricity used comes from non-renewable sources. This has led to growing concerns about the cryptocurrency’s environmental footprint.
2.2 Carbon Emissions and Environmental Impact
The carbon footprint of cryptocurrencies depends largely on the energy mix used in mining. In regions where electricity is generated from coal or other fossil fuels, the environmental impact is particularly high. This has sparked debates about the sustainability of Proof of Work-based cryptocurrencies and their long-term effects on the planet.
- Why It Matters: The environmental impact of cryptocurrency could influence regulatory decisions and public perception. As the world moves towards more sustainable practices, digital currencies must address their environmental challenges to remain viable.
3. The Push for Greener Alternatives: Proof of Stake and Beyond
In response to concerns about energy consumption, the cryptocurrency industry is exploring greener alternatives to Proof of Work. These alternatives aim to reduce the environmental impact of blockchain technology while maintaining security and decentralization.
3.1 Proof of Stake (PoS): A More Sustainable Consensus Mechanism
Proof of Stake (PoS) is an alternative consensus mechanism that requires validators to hold and “stake” a certain amount of cryptocurrency to participate in network validation. Unlike Proof of Work, PoS does not require energy-intensive computations, significantly reducing the energy consumption of the network.
- Example: Ethereum is currently transitioning from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake with its Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. This shift is expected to reduce Ethereum’s energy consumption by up to 99%, making it a much more sustainable blockchain.
- Why It Matters: The adoption of Proof of Stake and other energy-efficient consensus mechanisms could significantly reduce the environmental impact of cryptocurrencies, helping them align with global sustainability goals.
3.2 Layer 2 Solutions: Reducing the Environmental Impact
Layer 2 solutions, such as the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and zk-Rollups for Ethereum, are designed to improve the scalability and efficiency of blockchain networks. By processing transactions off-chain and then settling them on the main blockchain, these solutions can reduce the overall energy consumption of the network.
- Why It Matters: Layer 2 solutions not only enhance transaction speed and reduce costs but also contribute to a more sustainable blockchain ecosystem by minimizing the energy required for transaction validation.
3.3 The Role of Renewable Energy in Mining
Some cryptocurrency mining operations are now turning to renewable energy sources to power their activities. Solar, wind, and hydropower are increasingly being used by mining farms, particularly in regions with abundant renewable resources.
- Example: Several mining operations in Iceland and Canada use geothermal and hydroelectric power, respectively, to reduce their carbon footprint.
- Why It Matters: The shift to renewable energy in mining is a crucial step towards reducing the environmental impact of cryptocurrency. As more mining operations adopt green energy, the overall sustainability of the crypto industry could improve significantly.

4. The Future of Sustainable Blockchain: Innovations and Challenges
While progress is being made towards a greener cryptocurrency industry, several challenges remain. Achieving true sustainability will require ongoing innovation and collaboration between developers, miners, and policymakers.
4.1 Sustainable Blockchain Projects
Several blockchain projects are emerging with a focus on sustainability. These projects aim to reduce energy consumption, enhance efficiency, and promote environmental responsibility within the crypto industry.
- Example: Algorand is a blockchain platform that uses a unique consensus mechanism called Pure Proof of Stake (PPoS), which is designed to be energy-efficient and scalable. The project has also committed to being carbon-neutral by offsetting its emissions.
- Why It Matters: The development of sustainable blockchain projects is essential for the long-term success of the crypto industry. These projects demonstrate that it is possible to build environmentally responsible digital technologies.
4.2 Challenges to Achieving Sustainability
Despite the progress being made, there are still significant challenges to achieving sustainability in the cryptocurrency industry. These include the high initial energy demands of PoW networks, the slow adoption of renewable energy, and the need for global cooperation in setting environmental standards for blockchain technology.
- Why It Matters: Overcoming these challenges will be critical for the future of cryptocurrency. Without addressing these issues, the industry could face increased regulatory pressure and negative public perception, which could hinder its growth and adoption.
The Path to a Greener Future for Cryptocurrency
The environmental impact of cryptocurrency is a complex issue that requires thoughtful solutions and collective action. As digital currencies continue to grow in popularity, the push for more sustainable blockchain technologies is becoming increasingly important. From adopting energy-efficient consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake to exploring renewable energy options for mining, the cryptocurrency industry is beginning to address its environmental challenges. However, achieving true sustainability will require ongoing innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to balancing technological advancement with environmental responsibility.
For more insights and detailed guides on sustainable blockchain practices and environmental impact, visit our Cryptocurrency Comparisons Guides.
Stay Updated
For the latest updates on cryptocurrency sustainability and environmental impact, follow us on:
Stay informed with the latest strategies and developments in the world of cryptocurrency at FreeCoins24.io
Special Offer
Ready to invest in sustainable blockchain technologies? Sign up on Bybit today and take advantage of up to $30,000 in deposit bonuses. Discover a secure and eco-friendly way to trade digital assets.